Online shopping provides a quick and convenient way to purchase products, and this is especially true for the...
Hydrogel Dressings
Hydrogel dressings are an advanced wound care product. They are best known for creating an optimal, moist environment to aid in healing wounds. This dressing is semi-occlusive, keeping out bacteria while transferring vapor. Its semi-transparent construction allows some wound observation. Because the dressing contains mostly water, it does not stick to the wound. The major ingredients found in these dressings is deionized water, glycerin, and othe
Guide to Hydrogel Dressings
Hydrogel wound dressings are water-based or glycerin-based wound dressings. Manufacturers also include other ingredients such as allantoin, aloe barbadensis gel, diazolidinyl urea, sodium polyacrylate, propylene glycol USP, propylene glycol tetrasodium EDTA, hyaluronic acid, sodium metabisulfite FCC, methylparaben, methylparaben NF, propylparaben, propylparaben NF, propylparaben NFPEG-4 Olivate, PEG-60 hydrogenated castor oil, hyaluronic acid, sodium metabisulfite FCC, and tocopherol acetate. Hydrogel dressings with higher concentrations of glycerin offer improved absorption, bacteriostatic activity, and extended duration between bandage changing.
Hydrogel comes in several forms to choose from, including amorphous gel, impregnated gauze pads, cut-to-fit sheets, border dressings, or fillers. It also comes blended with zinc, Leptospermum, silver, and alginate to promote cell division and for infection control. This dressing absorbs exudate and provides autolytic debridement. It passes water vapor while protecting the wound from harmful airborne particles. The dressing stays in contact with the wound. Most often, a secondary dressing keeps the dressing in place. Some dressings are available with adhesive borders.
Indications
- minor burns
- skin tears
- abrasions
- skin grafts
- sloughy wounds
- necrotic wounds
- neonatal extravasation and excoriation
- diabetic ulcers
- pressure sores
- surgical wounds
Contraindications
- peripheral vascular disease in the presence of gangrenous tissue
- heavy exudate
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- promotes a moist environment
- provides autolytic debridement
- offers moderate absorbency
- helps reduce pain
- transparent options provide visual of wound
- rehydrate devitalized tissue
- promotes autolysis
- high moisture vapor transmission
- autolytic debridement
- light exudate draining
- Rehydrates necrotic eschar
Disadvantages
- not for use on heavy exuding wounds
- may cause maceration to adjacent skin
- may require a secondary dressing
FAQ's
How do you use this dressing?
These wound care products help regulate fluid exchange on wound surfaces. They maintain a moist environment for wound healing.
What is a hydrogel used for?
This type of dressing provides autolytic debridement for necrotic wounds. It promotes granulation and wound healing while offering a warm and moist wound environment to promote healing. It offers light to moderate exudation.
How do hydrogel bandages work?
The design of these dressings employs a thin mesh impregnated with a gel. The gel interacts with the wound to provide a moist wound environment. It also absorbs exudate into the gel, away from the wound.
How do you use hydrogel sheet dressing?
Sheet dressings offer significant flexibility for patient wound care. They may be cut-to-fit the size of the wound. A secondary dressing holds the dressing in place. Replace the dressing every 1 to 4 days.
When should you use hydrogel dressings? What kind of wound is hydrogel used for?
This type of dressing is best for the following wound types:
- Full thickness wounds
- Partial thickness wounds
- Dry wounds
- Radiation damaged tissue and skin
- Minor first- and second-degree burns
- Stage II to IV pressure ulcers
How long does a hydrogel dressing last?
These dressing should last from one to four days between changes.
What are the types of Hydrogel dressings?
Below is a list of the different types of hydrogel wound care products.
Type |
Use |
Product Example |
|---|---|---|
Hydrogel Dressings |
mends wound cavities |
|
Hydrogel Pads |
semi-occlusive dressing |
Medela Tender Care Hydrogel Pad |
Hydrogel Ointments |
prevent scabs, reduce scarring |
|
Hydrogel Sheets |
soft, flexible cut-to-fit |
|
Hydrogel Bandages |
cuts and partial-thickness burns |
|
Hydrogel Wound Gel |
natural barrier |
|
Hydrogel Filler |
mends wound cavities |
|
Amorphous Hydrogel |
malleable, free-flowing gel |
|
Hydrogel Island Dressing |
adhesive border |
DeRoyal Aquasorb Hydrogel Dressing |
Impregnated Hydrogels |
glycerine formulation will not dry out |
Top Manufacturers and Brands
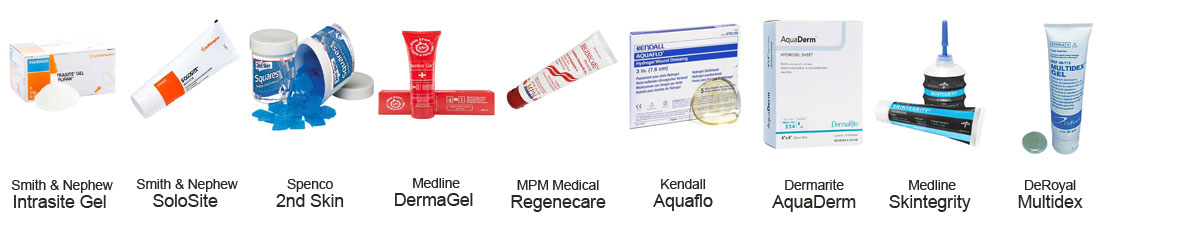
Ranking the Top Ten Best Hydrogel Dressings (by sales)
- Smith & Nephew Intrasite Gel
- Smith & Nephew SoloSite
- Spenco 2nd Skin
- Medline DermaGel
- MPM Medical Regenecare
- Kendall Aquaflo
- Dermarite AquaDerm
- Medline Skintegrity
- DeRoyal Multidex Gel
- Derma Sciences DermaGran B
- 3M Tegaderm Hydrogel
Manuals and Documents
-
 Francesko, Antonio, Petya Petkova, and Tzanko Tzanov. "Hydrogel dressings for advanced wound management." Current medicinal chemistry 25.41 (2018): 5782-5797.
Francesko, Antonio, Petya Petkova, and Tzanko Tzanov. "Hydrogel dressings for advanced wound management." Current medicinal chemistry 25.41 (2018): 5782-5797. -
 Kamoun, Elbadawy A., El-Refaie S. Kenawy, and Xin Chen. "A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings." Journal of advanced research 8.3 (2017): 217-233.
Kamoun, Elbadawy A., El-Refaie S. Kenawy, and Xin Chen. "A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings." Journal of advanced research 8.3 (2017): 217-233. -
 Rosiak, Janusz M. "Hydrogel dressings." 1991. 271-299.
Rosiak, Janusz M. "Hydrogel dressings." 1991. 271-299.
-
 Jones, Annie, and David Vaughan. "Hydrogel dressings in the management of a variety of wound types: A review." Journal of Orthopaedic nursing 9 (2005): S1-S11.
Jones, Annie, and David Vaughan. "Hydrogel dressings in the management of a variety of wound types: A review." Journal of Orthopaedic nursing 9 (2005): S1-S11. -
 Lay-Flurrie, Karen. "The properties of hydrogel dressings and their impact on wound healing." Prof Nurse 19.5 (2004): 269-273.
Lay-Flurrie, Karen. "The properties of hydrogel dressings and their impact on wound healing." Prof Nurse 19.5 (2004): 269-273. -
 Vowden, Kathryn, and Peter Vowden. "Wound dressings: principles and practice." Surgery (Oxford) 35.9 (2017): 489-494.
Vowden, Kathryn, and Peter Vowden. "Wound dressings: principles and practice." Surgery (Oxford) 35.9 (2017): 489-494.
-
 Corkhill, Philip H., Colin J. Hamilton, and Brian J. Tighe. "Synthetic hydrogels VI. Hydrogel composites as wound dressings and implant materials." Biomaterials 10.1 (1989): 3-10.
Corkhill, Philip H., Colin J. Hamilton, and Brian J. Tighe. "Synthetic hydrogels VI. Hydrogel composites as wound dressings and implant materials." Biomaterials 10.1 (1989): 3-10. -
 Seow, Wei Yang; Salgado, Giorgiana; Lane, E. Birgitte; Hauser, Charlotte A. E. (2016-09-07). "Transparent crosslinked ultrashort peptide hydrogel dressing with high shape-fidelity accelerates healing of full-thickness excision wounds" (PDF). Scientific Reports. 6: 32670
Seow, Wei Yang; Salgado, Giorgiana; Lane, E. Birgitte; Hauser, Charlotte A. E. (2016-09-07). "Transparent crosslinked ultrashort peptide hydrogel dressing with high shape-fidelity accelerates healing of full-thickness excision wounds" (PDF). Scientific Reports. 6: 32670
Hydrogel Wound Dressing Video (3:16 minutes)















Login and Registration Form