Online shopping provides a quick and convenient way to purchase products, and this is especially true for the...
Hydrocolloid Dressings - Pads, Foam, Gel, Alginate, Silver
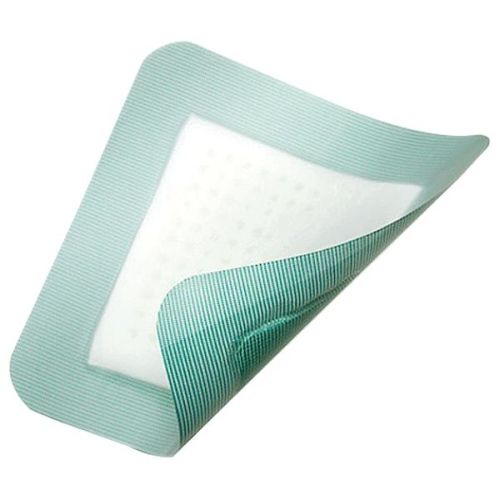
Hydrocolloid dressings are an advanced wound dressing constructed with pectin, carboxymethylcellulose, and polymers. Some dressings have an adhesive added to the border, laminated to film or foam. They are generally used for moderately draining wounds. What makes these dressings unique is their soft, absorptive wafers that become gel-like over time to help with the healing process. Our selection includes quality products from top brands.
Wound Healing Benefits of Hydrocolloid Dressings
These dressings offer many advantages for wound healing. Its design is waterproof and self-adhering. They repel water and seal the wound from external contaminants. Many of these dressings are self-adhesive to the skin around the wound. They absorb light to moderate exudate and are available in many different shapes and sizes. These dressings also come in different thicknesses. Dressing changes are less frequent than with many other dressings, requiring changes only every 3 to 5 days. Fewer changes reduce wound trauma and patient anxiety often experienced with dressing removal and replacement.
Types of Dressings
- Hydrocolloid Pads
- Thin Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Adhesive
- Silver Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Gel Bandage
- Hydrocolloid Sheet
- Alginate Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Sacral Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Foam Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Ointment
- Transparent Hydrocolloid
- Occlusive Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Water Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Acne Dressing
Construction
Gelatin
Pectin
Film Backing
Foam Backing
Opaque
Transparent
Indications
Partial to full thickness wounds
Granular wound
Necrotic wound
Moist or dry wound sites
Low to moderate draining wounds
Properties
Flexible and Body Conforming
Easy Application
Easy Removal
Light to Moderate Absorption
Does not Adhere to Wound
Occlusive
Contraindication
Infected wounds
Diabetic patients
Wound Types
Partial Thickness
Full Thickness
Low to Moderate Exudate
Granular
Necrotic
Dressing Characteristics
Occlusive
Flexible
Adheres to the skin, not the wound
Absorbs low to moderate exudate
Opaque
Advantages
- Promotes a moist environment for healing
- Provides autolytic debridement of necrotic wounds
- Highly absorbent
- Waterproof
- Fewer dressing changes (3 to 7 days)
- Offers faster healing
- Offers less pain
- Lowers risk of infection (impermeable to external contaminants)
- Will not traumatize skin upon removal
- Easy to apply
- Does not adhere to the wound
- Some are adhesive-dressings that adhere to surrounding skin to seal off the wound
- Flexible and conforming
Product Characteristics
Debridement: Autolytic
Moisture Management: light - moderate exudate; high vapor transmission; maintains moist environment
Wound Protection: occlusive; keeps out contaminates; impermeable to water; reduces infection risk
Conforming Bandages: flexible; body conforming
Change Frequency: 3 to 5 day; easy dressing changes; does not stick to wounds
Infection or Odor Control: no
Disadvantages
- Not for wounds with heavy exudate
- Not for infectious wounds
- May cause hypergranulation
- Possible skin maceration
- May promote the growth of anaerobic bacteria
- Not the best choice for patients with fragile skin
- Maybe challenging to stay in position
- Sometimes produces odor
- Not for use upon foot wounds of diabetic patients
FAQ's
What is a hydrocolloid dressing?
This wound care product is known for its flexibility and its occlusive design. It repels water and keeps out harmful substances, including bacteria. The bandage offers a moist wound environment to promote healing.
What are hydrocolloid dressings used for?
This dressing treats partial and full thickness wounds. It is a very flexible dressing that contours to the body, making it a good choice for awkward areas such as elbows and heels.
- autolytic debridement
- light to moderate exudate
- maintains a moist wound environment
- thermal insulation
- impermeable to water
- bacteria barrier
- reduces infection rates
- conforming bandage
Types of wounds served.
- Burns
- Pressure Ulcers
- Blisters
- Boils
- Sutures
- Abrasions
When should hydrocolloid dressings be used?
This wound treatment protects grandular and necrotic wounds. It should not be used on infected wounds unless it has an added antimicrobial agent such as silver.
Types of Hydrocolloid Dressings
- Gelatin
- Pectin
- Film Backing
- Foam Backing
- Transparent
- With or Without Border
Ranking the Best Hydrocolloid Dressings (by sales)
- 3M Tegaderm
- ConvaTec DuoDERM
- 3M Nexcare
- Coloplast Comfeel
- Medline Exuderm
- Coloplast Contreet
- Hollister Restore
- Smith & Nephew RepliCare
- Systagenix Nu-Derm
- DermaSciences Medihoney
- DermaRite DermaFilm
- Hartmann USA Flexicol
Medical Studies
 Xiao-Qin He, Hong-Lin Chen, Hydrocolloid vs Gauze Dressings in Treating Pressure Ulcers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Wounds. 26.9 (2014): E60-64.
Xiao-Qin He, Hong-Lin Chen, Hydrocolloid vs Gauze Dressings in Treating Pressure Ulcers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Wounds. 26.9 (2014): E60-64.  Sood, Aditya, Mark S. Granick, and Nancy L. Tomaselli. "Wound dressings and comparative effectiveness data." Advances in wound care 3.8 (2014): 511-529.
Sood, Aditya, Mark S. Granick, and Nancy L. Tomaselli. "Wound dressings and comparative effectiveness data." Advances in wound care 3.8 (2014): 511-529. Colwell, Janice C., Marquis D. Foreman, and Jeffrey P. Trotter. "A comparison of the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of two methods of managing pressure ulcers." Decubitus 6.4 (1993): 28-36.
Colwell, Janice C., Marquis D. Foreman, and Jeffrey P. Trotter. "A comparison of the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of two methods of managing pressure ulcers." Decubitus 6.4 (1993): 28-36. Singh, Aparajita, et al. "Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on hydrocolloid occlusive dressing versus conventional gauze dressing in the healing of chronic wounds." Asian journal of surgery 27.4 (2004): 326-332.
Singh, Aparajita, et al. "Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on hydrocolloid occlusive dressing versus conventional gauze dressing in the healing of chronic wounds." Asian journal of surgery 27.4 (2004): 326-332. Helfman, Todd, Liza Ovington, and Vincent Falanga. "Occlusive dressings and wound healing." Clinics in dermatology 12.1 (1994): 121-127.
Helfman, Todd, Liza Ovington, and Vincent Falanga. "Occlusive dressings and wound healing." Clinics in dermatology 12.1 (1994): 121-127.















Login and Registration Form