Updated: February 3, 2023
Oxygen is essential medicine. It reduces mortality rates in childhood pneumonia1 2 and supports aging adults with respiratory illnesses. Oxygen concentrators support many recovering from an accident or surgery. There are many parts to oxygen concentrators that require maintenance and replacement. Establishing a system to keep home and portable oxygen concentrators operating with an inventory of spare parts and consumables is essential for maintaining these devices in good working order.3 This article explores the common replaceable components and replenishable consumables for oxygen concentrators and provides product examples of the top-selling replacement parts.
Concentrator Air Filters

Oxygen Concentrator Filters are of two types—external and internal filters. External filters, often referred to as particle filters, screen for foreign contaminants like dust, dander, and hair that can damage or inhibit the machine’s operation. Internal filters screen for bacteria to provide high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA). Typically, HEPA filters trap pollen, viruses, bacteria, mold, and other harmful microparticles.
List of the Types of O2 Filters
- Inlet filter
- Intake filter
- Internal filter
- Air inlet filter
- HEPA filter
How Often Should Oxygen Concentrator Filters Be Changed?
Manufacturers recommend every 6 to 12 months, depending upon environmental conditions. Dusty conditions require more frequent changes. Consult the device’s user instructions for more specific guidance.
Where Is the Filter on an Oxygen Concentrator?

| Respironics Millennium M10 | Respironics EverFlo |

| DeVilbiss 5-Liter | Inogen G3 | SeQual Eclipse |
Where to Buy Oxygen Concentrator Filters for Sale?
Some specialized oxygen concentrator repair stores are in major metropolitan areas that people can drive to and purchase. However, having the right filter for a particular machine in stock is hit-and-miss since most stores only supply the filters for the brands of devices they sell. Call ahead to verify. These repair and parts facilities often have to order the filter with delivery in one to two weeks. Online stores are more reliable with less expensive filters for all major brands and usually deliver in four to seven days right to your door.
How to Replace an Oxygen Concentrator Filter?
Most external filters have foam construction and are inexpensive. Although they may be washed, dried, and reused, most people simply replace them and do not deal with the hassle of cleaning. Below are the typical steps for replacing an inlet concentrator filter.
For internal filter replacement, consult the owner’s manual or consider a local O2 repair facility.
Nasal Cannula
A nose cannula is tubing that supplies supplemental oxygen to a patient. One end of the tubing connects to an oxygen tank or concentrator, while the other end splits into two separate tubes that form a headset looping around both ears to hold the cannula in place. The split tubing joins together into two nasal prongs. These prongs insert into the nostrils, delivering oxygen to the patient. The image below depicts the parts of the top-selling Teleflex Hudson RCI Softech Nasal Cannula.
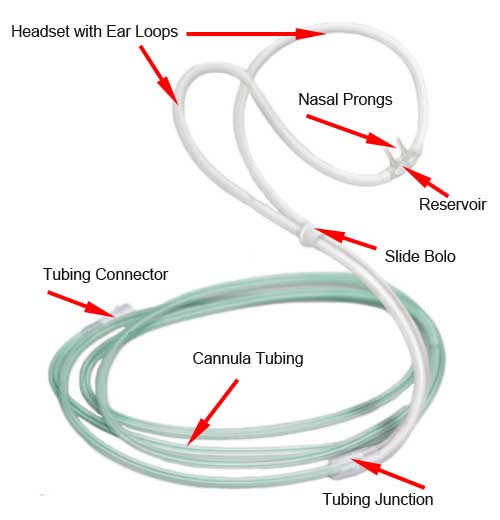 List of O2 Cannula Parts
List of O2 Cannula Parts
- Nasal Cannula Tubing
- Nasal Cannula Prongs
- Nasal Cannula Reservoir or Oxymizer Pendant
- Slide Bolo
- Tubing Connector
- Tubing Junction
- Ear Loops
- Headset
What Are the Types of Nasal Cannulas?
O2 cannulas come in three different sizes—infant, pediatric, and adult. The prongs come in four options—curved or straight and tapered or flared. The tubing itself comes in two options—low flow (1-6 liters per minute) or high flow (7 or more liters per minute). There are tubing options such as kinkless, safety, and soft cannula tubing for less intrusiveness. There are also cannulas with conservers, reservoirs, or oxymizers that reduce the need for an oxygen mask and provide oxygen therapy while eating, drinking, or talking.
High-Flow vs. Low-Flow Nasal Cannula
|
High Flow |
Low Flow |
|
Usually requires humidification |
Less intrusive |
|
Requires high-output devices |
Standard size tubing |
|
Often the air is heated |
Lower cost |
|
Wide bore tubing |
More readily available |
|
Difficult to tolerate for long periods |
|
A high-flow cannula is for patients who require a significant amount of oxygen to survive. As indicated above, high flow provides for 7 or more liters of oxygen per minute. To achieve this level of O2 flow, patients use a larger oxygen concentrator or oxygen cylinders with higher outputs. The tubing has a larger diameter to facilitate increased oxygen flows. Low flow provides up to 6 liters and has a narrow diameter. The chart below depicts the critical differences between high-flow and low-flow nasal cannulas.
Product Examples:
How Often Should You Change a Nasal Cannula?
Patients who use oxygen therapy 24/7 should replace their cannula every two weeks. Others who use their cannula only a few hours daily should replace it monthly to bi-monthly. People in high-humidity areas should replace their cannulas more frequently.
How do you put on nasal cannula? (2:27 minutes)
Nasal Cannula Advantages and Disadvantages
Oxygen cannula offers numerous benefits with few detriments to respiratory patients. Below is a list of the advantages and disadvantages of using a nasal oxygen cannula.
|
O2 Cannula Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
More comfortable than masks |
Max FiO2 is around .40 with a cannula |
|
Less intrusive |
Not for patients with significant respiratory distress |
|
Accommodates claustrophobic patients |
Requires water traps on tubing in humid environments or colder weather |
|
Adaptive to home therapy patients |
Higher flow rates are less comfortable |
|
Effective oxygen delivery for most patients |
Nasal delivery does not work well for congested patients |
|
Increases patient compliance |
|
|
Fewer humidification requirements |
|
|
Accommodates eating and drinking |
|
|
Permits talking |
|
|
|
|
Oxygen Tubing
Tubing connects the oxygen source, such as an oxygen cylinder or concentrator machine, to the cannula that attaches to the patient. Both ends of the tubing have connectors that link to a concentrator, oxygen tank regulator or conserver, water traps, and nasal cannula. Usually, O2 tubing does not exceed 50 feet. The more length that the tubing has, the less oxygen output to the end user. Long tubing lengths accommodate greater freedom of movement throughout a home; however, longer lengths also decrease the amount of oxygen that reaches the patient. Larger output concentrators or regulators that offer higher flows can often compensate for longer tubing. Still, caution should prevail using long tubing lengths that may not support the patient with adequate oxygen volume.
List of Common Oxygen Tubing Lengths
- 6 feet
- 7 feet
- 10 feet
- 14 feet
- 25 feet
- 50 feet
Product Examples:
Salter Labs Three Channel Oxygen Tubing
Sure Flow Oxygen Tubing
Green Tubing vs. Transparent Tubing
Colored oxygen tubing has more visibility than transparent tubing. This allows the patient and others to better see the tubing to avoid a trip hazard. This enhanced tube visibility makes it safer for everyone in the home.
Product Example:
AirLife Green Oxygen Supply Tubing
Oxygen Humidifier Supplies
Oxygen humidifier products include bubble humidifiers, tubing adapters, and water traps. Bubble humidifiers supply water to be vaporized and injected into the concentrated oxygen. These humidifier bottles store distilled water that is aerosolized to mix with breathable air. Patients who experience dryness or discomfort associated with oxygen therapy benefit significantly from these devices, particularly patients on high-flow oxygen. Tubing adapters provide a connection from the bubble humidifier to the oxygen concentrator. The adapters consist of short tubing with connectors on each end. Water traps collect excess moisture within the oxygen tubing that runs from the concentrator to the user. Often, and especially during cold weather, moisture in the tubing condenses and forms water droplets that can make breathing difficult. Water traps insert into the oxygen tubing to prevent water from reaching the patient.
Product Examples:
Salter Labs 6 PSI Low Flow Bubble Humidifier
AirLife Oxygen Humidifier Bottle 370 mL
Invacare Humidifier Adapter
Inline Water Trap
Nasal Moisturizer
A good nasal moisturizer can help people who experience dryness. Moisturizers can restore dry skin and keep skin from becoming irritated and chafed. Often, these lotions and creams work immediately on contact. They can reduce friction from contact with the cannula and speed healing.
Product Examples:
Cann-Ease Nasal Moisturizer
Ayr Saline Nasal Gel
O2 Batteries
Portable oxygen concentrators require batteries for operation, particularly while away from an AC power source. Extra batteries for portable oxygen concentrators offer patients extended use time while away from home. Portable batteries come in various sizes, shapes, and storage capacities and are model-specific. Lithium ion usually constitutes the battery core due to its high storage capacity and exceptional charge capacity.
Batteries are machine-specific. One battery brand will not work on another oxygen concentrator brand. For instance, the DeVilbiss iGo battery is not compatible with an Inogen concentrator. Many concentrator users buy extra batteries to obtain increased service while away from an AC power source. While traveling, long periods of in-flight oxygen service may require several batteries to accommodate the flight duration. Many airlines require additional backup batteries to address any unforeseen emergencies before the oxygen patient can board the plane.
Below are some of the best-selling replacement batteries for sale.

List of Best Oxygen Concentrator Batteries
- DeVilbiss iGo
- SimplyGo
- Inogen G4
- SeQual eQuinox
Battery Charger
Battery chargers provide the means to charge a battery external to the concentrator. While plugged into an AC outlet, most portable oxygen concentrators can charge the battery. The addition of an external charger allows the user to be out and about using their concentrator with one battery while another battery charges on the external charger. Below are some of the best-selling oxygen concentrator battery chargers for sale.

List of Top-Ranking O2 Concentrator Battery Chargers
- Inogen One
- AirSep
- Respironics EverGo
- O2 Concepts Oxlife
- Respironics SimplyGo
Sieve Beds
Oxygen concentrators operate with sieve beds that filter out nitrogen from the air around us which constitutes 80% nitrogen and 20% oxygen. Sieve beds screen out nitrogen to deliver oxygen of 85% or higher to the patient. Sieve beds can work satisfactorily for one to two years and then need replacing. When the oxygen output is less than what the doctor prescribes, it may be time to replace the sieve beds. Several manufacturers of oxygen concentrators make sieve bed replacement almost as simple as replacing batteries. Below are some replaceable sieve beds for sale.

List of Top Concentrator Sieve Bed Replacements
- GCE Zen-O
- AirSep
- Inogen
- Invacare Perfecto2
Footnotes
- 1 Duke, T., et al. Oxygen is an essential medicine: a call for international action [Unresolved issues]. The International journal of tuberculosis and lung disease 14.11 (2010): 1362-1368. (Last Accessed April-15-2021)
- 2 Matai, Sens, et al. Implementing an oxygen program in hospitals in Papua New Guinea. Annals of tropical paediatrics 28.1 (2008): 71-78. (Last Accessed April-15-2021)
- 3 World Health Organization. Technical Specifications for Oxygen Concentrators: WHO Medical Device Technical Series. World Health Organization, 2016. (Last Accessed April-15-2021)


Login and Registration Form