Low Flow Oxygen Concentrator Comparison and Review
Updated: December 3, 2020

Low Flow Oxygen Concentrator Review Update 2020
Low Flow Oxygen Concentrators provide continuous oxygen flow of fewer than 5 liters per minute (LPM). These oxygen machines are designed to accommodate both adults and pediatrics. Since most oxygen patients require only 2 liters of oxygen or less per minute, these low flow concentrators have an extensive application. Some of the low flow oxygen concentrators for sale target the pediatric market since children have a smaller lung capacity. Unfortunately, "low flow" in the mind of many consumers is not an adult oxygen concentrator. However, low flow oxygen concentrators are capable of serving both children and adults and offer many advantages that bigger higher-flow concentrators are unable to provide.
This oxygen concentrator comparison update for 2020 examines the top low-flow home oxygen concentrators on the market, offering 2 to 3 liters of oxygen therapy per minute. This update, however, finds only one of these pediatric concentrators still in production-the Respironics SimplyFlo 2 Liter Oxygen Concentrator. Caire discontinued the VisionAire 2 and the VisionAire 3 Liter Oxygen Concentrator. At the time of this update, there are still a few VisionAire 3's left in inventory to purchase; however, there are no more VisionAire 2 models available. Since only two models are currently available to buy, the SimplyFlo 2 and the VisionAire 3, a review follows below. A side-by-side comparison of these two low flow home oxygen concentrators displays below the review. At the bottom of this page are links to research studies regarding Low-Flow Oxygen Therapy.
Additional oxygen concentrator rankings, reviews, and comparison charts can be viewed by clicking on the links below:
- High Flow Oxygen Concentrator Comparison - examines 8- and 10-liter oxygen generators.
- Compare Home Oxygen Concentrators with 5 Liters - compares the top ten home oxygen concentrators on the market.
- Portable Oxygen Concentrator Reviews - offers product details by brand.
- Pulse Flow Portable Oxygen Concentrator Review - compares the top portable oxygen machines on the market.
- Continuous/Pulse Flow Portable Concentrator Rankings - rank orders the top concentrators that offer both pulse and continuous flow oxygen.
- What is a Continuous Flow Portable Oxygen Concentrator?
- What is a Pulse Flow Oxygen Concentrator?
Best Performing Low Flow Oxygen Concentrator
Determining which concentrator offers the best performance is measured from four separate factors--continuous oxygen flow, oxygen concentration, outlet pressure and maximum operating altitude. The VisionAire 3 is the best performing low flow oxygen concentrator. It offers 3 liters of continuous oxygen therapy per minute with a maximum outlet pressure of 25 psi. The VisionAire 2 matches the performance of the VisionAire 3 in every aspect except maximum oxygen flow, offering 2 liters instead of 3. The SimplyFlo ranks first for oxygen concentration levels with a slightly higher concentration range of 87 to 96%. All three concentrators can operate up to an altitude of 10,000 feet above sea level.
| Model | Continuous Oxygen Flow (max LPM) |
Oxygen Concentration |
Oxygen Outlet Pressure (max psi) |
Operating Altitude (feet above sea level) |
| VisionAire 3 | 3 | 87 to 95.5% | 25 | 10,000 |
| SimplyFlo | 2 | 87 to 96% | 6.4 | 10,000 |
Lowest Power Consumption
Usually, the smallest oxygen concentrator provides the lowest power consumption. Such is the case with the low-flow concentrators. The SimplyGo 2 concentrator consumes an average of 120 watts while operating. This power consumption is the second-best power usage for all home oxygen concentrators. Only the At Home concentrator with an average power usage of only 110 watts is better. VisionAire 3 uses 175 watts of power. The national average for the cost of a kilowatt per hour (KWH) is 0.1327 cents. (Source: Choose Energy, October 1, 2019, Electricity rates by state – the U.S. average is 13.27 cents per kilowatt hour, Last Accessed November 25, 2019)
The chart below displays the average watts per hour for each low-flow oxygen concentrator with the average daily cost and the average annual cost to operate. The average watts and costs displays for operating a 5-liter, 8-liter, and 10-liter concentrator as a comparison. The figures for the VisionAire 3, highlighted in gray, and the numbers for the SimplyFlo, highlighted in yellow, are significantly lower than the 5- through 10-liter machines. Oxygen patients that need 2 to 3 liters of oxygen can save from around $135 to $199 annually on their electric bill by purchasing a low-flow concentrator instead of a 5-liter concentrator. These same patients can save between $499 to $563 annually with a low-flow concentrator over a 10-liter concentrator. In other words, oxygen patients could buy a new low-flow concentrator every 2 to 5 years from just the savings on their electric bill.
Power Usage Comparison
| 10 Liter Average |
8 Liter Average |
5 Liter Average |
VisionAire 3 | SimplyFlo | |
| Average Watts (Per Hour) |
604 | 455 | 291 | 175 | 120 |
| Daily Watt Usage (operating 24 hours) |
14,496 | 102,920 | 6,984 | 4,200 | 2,880 |
| Average Daily Cost (0.1256 cents per KWH National Ave) |
$1.92 | $1.45 | $0.93 | $0.56 | $0.38 |
| Annual Watt Usage (24/7 Operation) |
5,294,664 | 3,988,530 | 2,550,906 | 1,534,050 | 1,051,920 |
| Average Annual Cost (0.1256 cents per KWH National Ave) |
$720.60 | $529.28 | $338.51 | $203.57 | $139.59 |
Lowest Noise
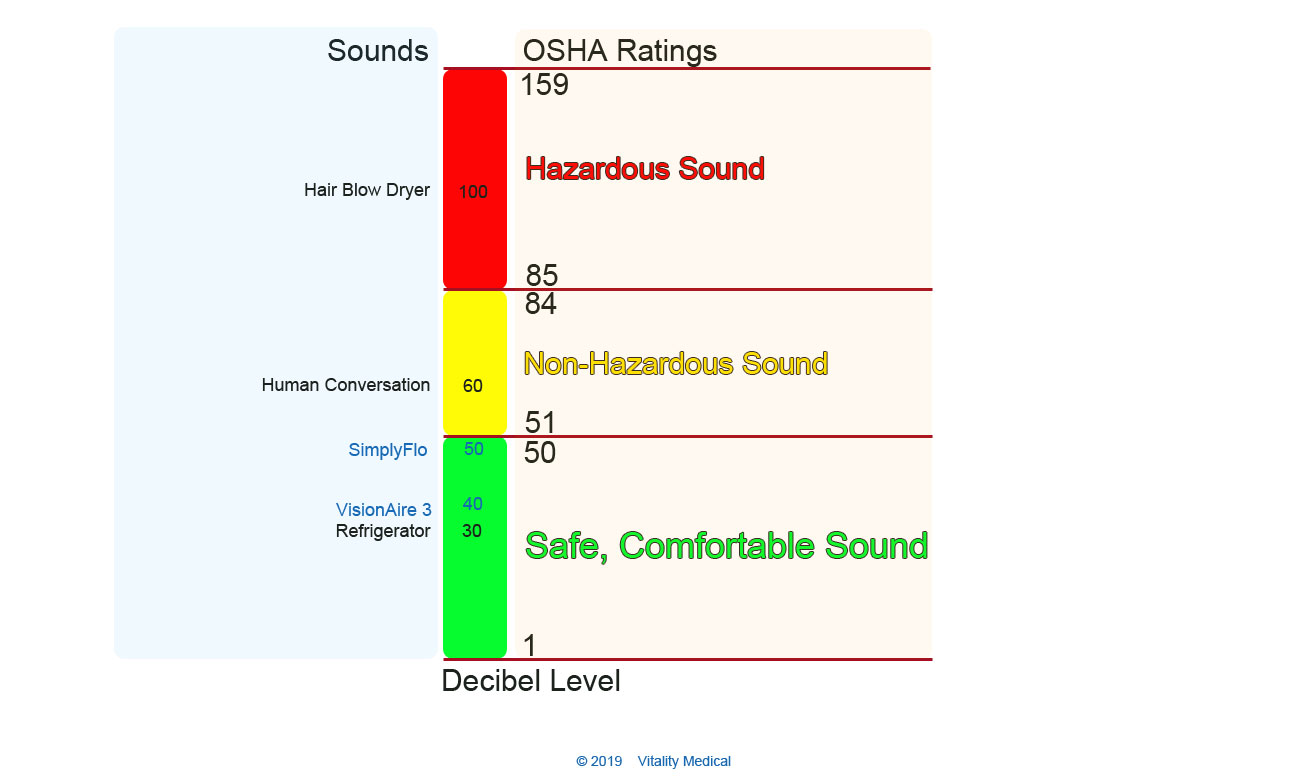
Noise measures sound pressure in decibel units. The OSHA Hearing Protection Guidelines consider decibel levels below 50 as safe and comfortable. Sound levels with decibels between 51 and 84 decibels are non-hazardous. Sound above 85 decibels is harmful.
Noise emissions of oxygen concentrators are generally lower than the sound of human conversation averaging 60 decibels. Oxygen patients do not want to be exposed to more noise than they have to. Both low-flow oxygen concentrators in this comparison have a decibel level at or below 50--the safe, comfortable zone. The VisionAire 3 concentrator takes the 1st place ranking with 40 decibels. The lightweight SimplyFlo generates 50 decibels of noise while operating. See the chart below for the noise level comparison of each low flow concentrator.
Noise Decibel Level Comparison
Smallest Size
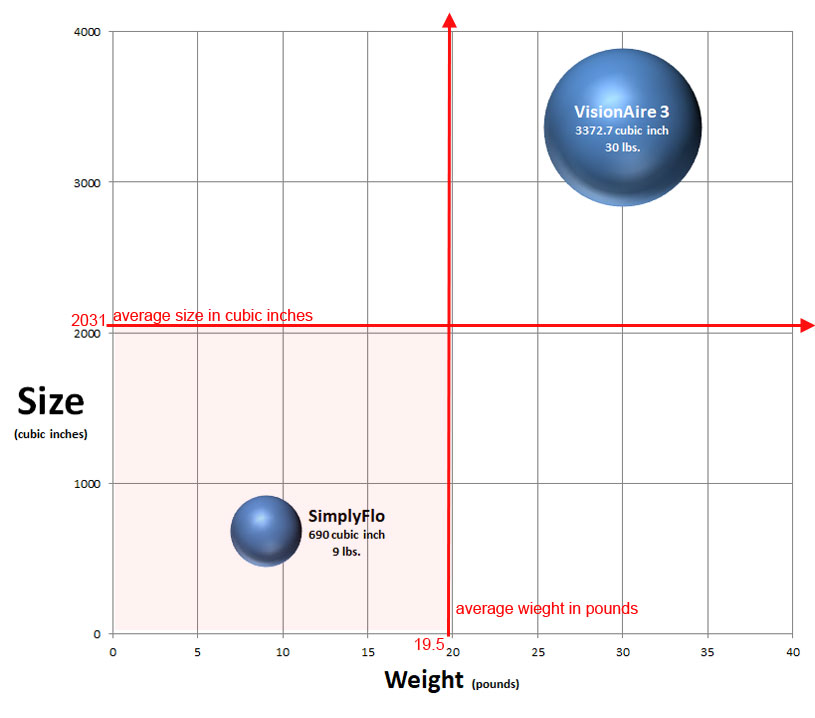
For oxygen delivery systems, smaller is better. Smaller sized oxygen concentrators take up less space and are easier to move from room to room. Weight is another critical factor. Pushing a heavy oxygen concentrator down a narrow hallway to another room can be less cumbersome with a more lightweight machine. Room-to-room mobility of an oxygen concentrator significantly increases with a smaller and lightweight concentrator. Since low-flow oxygen concentrators have smaller oxygen generators, they are more likely to have a smaller size and lower weight than the 5-liter concentrators or high-flow concentrators. The average profile for a 5-liter concentrator is 3,634 cubic inches, and the average weight is 35 pounds. Low-flow concentrators have an average size of 2,031 cubic inches and an average weight of 19.5 pounds. These figures represent a 56% reduction in size and weight. The SimplyFlo ranks number one for the smallest size and lowest weight low-flow home oxygen concentrator. The comparison chart below displays size and weight graphically for the two concentrators compared.
Bonus Features
The no maintenance feature of VisionAire 3 is a nice feature that is significant for many oxygen therapy patients. The VisionAire model comes with a flowmeter to view oxygen delivery. They also come with oxygen flow locking and overdraw protection. An optional oxygen sensor is available for the VisionAire 3 and is standard on the VisionAire 2 concentrator. The VisionAire 2 serves well as a pediatric oxygen concentrator and can dial down to a flow setting as low as 1/8 liter per minute for pediatric applications.
Best Low-Flow Oxygen Concentrator
The overall best home oxygen concentrator with low-flow oxygen delivery is the AirSep VisionAire 3. The VisionAire 3 ranks number one for maximum oxygen flow of 3 liters, number one for maximum outlet pressure, and number one for the lowest noise level. The VisionAire 3 comes with a standard 3-year warranty.
The Respironics SimplyFlo ranks first for oxygen concentration level, smallest size, most lightweight, and lowest power consumption. Its standard 2-year warranty can upgrade to 3 years for an additional fee, but only at the time of purchase. If size and weight are a significant concern, we would recommend the SimplyFlo over the VisionAire. If performance is a considerable concern, VisionAire 3 is the best choice.
Best Low-Flow Oxygen Concentrator
#1 Ranking for Best Oxygen Outlet Pressure - 25 psi
#1 Ranking for Highest Oxygen Flow - 3 LPM
#1 Ranking for Lowest Noise - 40 dBA
#1 Ranking for Longest Warranty
Operating Altitude Up To 10,000 (feet above sea level)
24/7 Operation
Made in the USA
Caire AirSep VisionAire 3
Oxygen Concentrator Comparison Chart Low Flow Machines
| Low-Flow Oxygen Concentrators |
 |
 |
|||
| Model | VisionAire 3 | SimplyFlo | |||
| Manufacturer | AS096-6 | 1076773 | |||
| Model # | AirSep | Respironics | |||
| Performance | |||||
| Continuous Oxygen Flow (max LPM) |
3 | 2 | |||
| Oxygen Concentration | 87% to 95.5% | 87 to 96% | |||
| Oxygen Outlet Pressure (max psig) |
25 | 6.4 | |||
| Operating Altitude (feet above sea level) |
10,000 | 10,000 | |||
| Size | |||||
| Cubic Size (inches) |
3372.72 | 690 | |||
| Width (inches) |
14.1 | 10 | |||
| Height (inches) |
20.8 | 11.5 | |||
| Depth (inches) |
11.5 | 6 | |||
| Weight (pounds) |
30 | 9 | |||
| Operating Factors | |||||
| Noise (dBA) |
40 | 50 | |||
| Average Power Consumption (watts) |
175 | 120 | |||
| Dependability | |||||
| Made in the USA | Yes | Yes | |||
| Warranty | 3 Yrs | 2 Yrs | |||
Medical Studies
-
 Fahlman A, Caulkett N, Woodbury M, Duke-Novakovski T, Wourms V. Low flow oxygen therapy from a portable oxygen concentrator or an oxygen cylinder effectively treats hypoxemia in anesthetized white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Zoo Wildl Med. 2014 Jun;45(2):272-7.
Fahlman A, Caulkett N, Woodbury M, Duke-Novakovski T, Wourms V. Low flow oxygen therapy from a portable oxygen concentrator or an oxygen cylinder effectively treats hypoxemia in anesthetized white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). J Zoo Wildl Med. 2014 Jun;45(2):272-7. -
 Marlowe, S. Oxygen Therapy. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. September, 2014.
Marlowe, S. Oxygen Therapy. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. September, 2014. -
 Weitzenblum E, Sautegeau A,Ehrhart M, Mammosser M, Pelletier A. Long Term Oxygen Therapy can Reverse the Progression of Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;131:493-498.
Weitzenblum E, Sautegeau A,Ehrhart M, Mammosser M, Pelletier A. Long Term Oxygen Therapy can Reverse the Progression of Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;131:493-498. -
 Morrison DA, Stovall JR. Increased Exercise Capacity in Hypoxemic Patients after Long Term Oxygen Therapy. CHEST. 1992;102:542-550.
Morrison DA, Stovall JR. Increased Exercise Capacity in Hypoxemic Patients after Long Term Oxygen Therapy. CHEST. 1992;102:542-550. -
 Heaton RK, Grant I, McSweeny AJ, Adams KM, Petty TL. Psychologic Effects of Continuous and Nocturnal Oxygen Therapy in Hypoxemic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Arch Intern Med.1983;143:1941-1947.
Heaton RK, Grant I, McSweeny AJ, Adams KM, Petty TL. Psychologic Effects of Continuous and Nocturnal Oxygen Therapy in Hypoxemic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Arch Intern Med.1983;143:1941-1947. -
 Nasilowsk J, Przybylowski T, Zielinski J,Chazan R. Comparing supplementary oxygen benefits from a portable oxygen concentrator and a liquid oxygen portable device during a walk test in COPD patients on long-term oxygen therapy. Respiratory Medicine. July 2008. Volume 102, Issue 7, Pages 1021–1025.
Nasilowsk J, Przybylowski T, Zielinski J,Chazan R. Comparing supplementary oxygen benefits from a portable oxygen concentrator and a liquid oxygen portable device during a walk test in COPD patients on long-term oxygen therapy. Respiratory Medicine. July 2008. Volume 102, Issue 7, Pages 1021–1025. -
 Chatburn, R, Lewarski J, McCoy R. "Nocturnal oxygenation using a pulsed dose oxygen conserving device compared to continuous flow oxygen." Respir Care March 2006;51(3): 252-256.
Chatburn, R, Lewarski J, McCoy R. "Nocturnal oxygenation using a pulsed dose oxygen conserving device compared to continuous flow oxygen." Respir Care March 2006;51(3): 252-256. -
 McCoy, R, Lewarski, J. "A test for clinical equivalency: A portable concentrator with integrated oxygen-conserving compared to continuous flow oxygen during nocturnal use." Respir Care November 2005; 51 (11).
McCoy, R, Lewarski, J. "A test for clinical equivalency: A portable concentrator with integrated oxygen-conserving compared to continuous flow oxygen during nocturnal use." Respir Care November 2005; 51 (11). -
 Agarwal, R, and Gupta, D. What are High-Flow and Low-Flow Delivery Systems? Stroke, 2005; 36: 2066-2067.
Agarwal, R, and Gupta, D. What are High-Flow and Low-Flow Delivery Systems? Stroke, 2005; 36: 2066-2067. - Singhal AB, Benner T, Roccatagliata L, Koroshetz WJ, Schaefer PW, Lo EH, nanno FS, Gonzalez RG, Sorensen AG. A pilot study of normobaric oxygen therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2005; 36: 797–802.
-
 Miller, Kenneth. High Flow Oxygen: Does It Make a Difference? RT Magazine. September 12, 2013.
Miller, Kenneth. High Flow Oxygen: Does It Make a Difference? RT Magazine. September 12, 2013. -
 Lenglet H, Sztrymf B, Leroy C, Brun P, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Humidified high flow nasal oxygen during respiratory failure in the emergency department: feasibility and efficacy. Respir Care. 2012;57(11):1873-8.
Lenglet H, Sztrymf B, Leroy C, Brun P, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Humidified high flow nasal oxygen during respiratory failure in the emergency department: feasibility and efficacy. Respir Care. 2012;57(11):1873-8. -
 Adult Oxygen Therapy Made Easy. Respiratory Therapy Cave. August, 2010.
Adult Oxygen Therapy Made Easy. Respiratory Therapy Cave. August, 2010. -
 Katsenos S, Constantopoulos S. Long-Term Oxygen Therapy in COPD: Factors Affecting and Ways of Improving Patient Compliance. Pulmonary Medicine. Volume 2011.
Katsenos S, Constantopoulos S. Long-Term Oxygen Therapy in COPD: Factors Affecting and Ways of Improving Patient Compliance. Pulmonary Medicine. Volume 2011. -
 Waterhouse JC, Nichol J, Howard P. Survey on domiciliary oxygen by concentrator in England and Wales. Eur Respir J, 1994, 7, 2021–2025.
Waterhouse JC, Nichol J, Howard P. Survey on domiciliary oxygen by concentrator in England and Wales. Eur Respir J, 1994, 7, 2021–2025. -
 Bliss, PL, McCoy, RW, Adams, AB. A bench study comparison of demand oxygen delivery systems and continuous flow oxygen. Respiratory Care. Volume 44, Issue 8, August 1999, Pages 925-931.
Bliss, PL, McCoy, RW, Adams, AB. A bench study comparison of demand oxygen delivery systems and continuous flow oxygen. Respiratory Care. Volume 44, Issue 8, August 1999, Pages 925-931. -
 Bliss PL, McCoy RW, Adams AB. Characteristics of demand oxygen delivery systems: maximum output and setting recommendations. Respir Care, 49 (2004), pp. 160–165.
Bliss PL, McCoy RW, Adams AB. Characteristics of demand oxygen delivery systems: maximum output and setting recommendations. Respir Care, 49 (2004), pp. 160–165. -
 Roberts CM, Bell J, Wedzicha JA, Comparison of the efficacy of a demand oxygen delivery system with continuous low flow oxygen in subjects with stable COPD and severe oxygen desaturation on walking. Thorax, 51 (1996), pp. 831–834,
Roberts CM, Bell J, Wedzicha JA, Comparison of the efficacy of a demand oxygen delivery system with continuous low flow oxygen in subjects with stable COPD and severe oxygen desaturation on walking. Thorax, 51 (1996), pp. 831–834,

Burt Cancaster, Author
Vitality Medical
7910 South 3500 East, Suite C
Salt Lake City,
UT
84121
(801) 733-4449
[email protected]
Vitality Medical
Login and Registration Form