Quick Summary:
Click a link to jump to the section.
Introduction
IV catheters are an important part of intravenous therapy equipment. They are essential for fluid delivery, medication administration, and blood collection.
This guide will provide a comprehensive IV catheter overview, as well as a needle gauge guide. Needle size — or gauge — affects flow rate, comfort, and suitability for specific medical procedures. We will outline common IV catheter needle sizes, color codes, and best-use scenarios.
Browse Vitality Medical infusion supplies and sets to support IV treatment in both professional and home healthcare environments.
1. Understanding IV Catheter Gauge Sizes
The range of needle sizes allows for different procedures to be performed effectively. Your choice will most likely fall between 14G to 26G catheter sizes.
A needle size comparison may help you decide which one works best for you. The larger the needle, the greater the IV flow capacity. The gauge will also affect insertion ease and infusion speed. Small needles help prioritize patient comfort and precision.
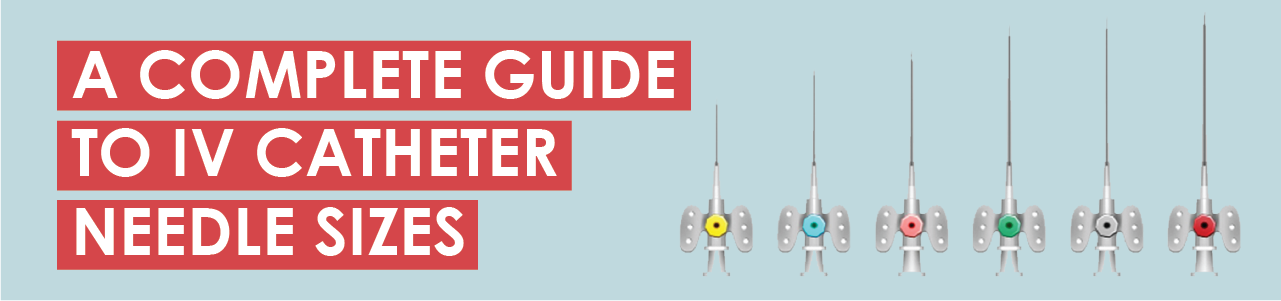
The word “gauge” refers to a needle’s outer diameter. IV gauge measurements can get confusing; keep in mind that the smaller the gauge number, the larger the needle. For instance, a 14-gauge needle has a catheter diameter of 2.10 mm. Meanwhile, a 26-gauge needle has a diameter of just 0.60 mm.1
A larger size needle, such as a 16- or 14-gauge, is ideal for quick or emergency administrations. You shouldn't use a smaller needle for blood transfusions to avoid damaging red blood cells. Rather, these are preferred for patients with tiny or fragile veins.2
2. Common IV Catheter Sizes and Color Codes
A universal hospital color coding system ensures medical staff select the right gauge for their patient. This system is essential, as it aids in quick catheter gauge identification during emergency care. Most facilities use infusion equipment labeling to organize sizes by colors.
Each gauge has a different use in healthcare settings. Consider this IV catheter color chart for needle size references:
- 14G (Orange): Trauma and rapid fluid replacement.
- 16G (Gray): Major surgery, ICU, and quick blood transfusions.
- 18G (Green): Routine blood administration and general infusions.
- 20G (Pink): Common adult IV, medications, and maintenance fluids.
- 22G (Blue): Elderly patients and smaller veins.
- 24G (Yellow): Pediatric patients, fragile veins, and slow infusions.
- 26G (Purple): Neonatal patients and tiny or damaged veins.

3. Factors That Determine Catheter Size Selection
Choosing an IV catheter size depends on factors like patient age, vein size, infusion type, and flow rate requirements. Larger gauges are a preferred choice for rapid fluid delivery. Smaller ones support fragile vein management or long-term therapy.
Gauges 14–20 are compatible with blood transfusion catheters. Because of their higher flow rate, large sizes are ideal for administering blood and thicker fluids.
Smaller sizes, such as 22-, 24-, and 26-gauges, help ensure precise insertion. This makes them better suited for elderly, neonatal, and pediatric IV insertion.
4. Flow Rate and Application Differences
Gauge size determines infusion flow rates. This is important because the fluid rate impacts hydration, blood transfusion, and emergency response.
Poiseuille’s law suggests that a flow rate rises with a larger tube radius and increased pressure. Shorter, wider tubing allows for faster infusion. Thus, flow rates drop with longer tubing and thin tube diameters.3
With a larger bore, the flow will be faster. This knowledge supports IV therapy efficiency and proper blood transfusion speed. Review patient needs and try to find a balance between comfort and efficiency in gauge selection.
In an emergency IV setup, always keep wide bore tubing and gauges available. For rapid fluid administration, you will want a larger size gauge (14G or 16G).
5. Material and Design Considerations
When selecting an IV catheter, the right material can make all the difference. Let’s look at polyurethane vs Teflon catheters. Consider the advantages of each:4
Teflon (PTFE):
- Chemical resistance
- Low friction coefficient
- High temperature resistance
Polyurethane:
- Highly flexible
- Abrasion resistance
- Impact resistance
When choosing, consider safety IV catheter design features. You can add safety needles, wings, and blood-control valves to improve security and handling.
Needle safety technology can help improve patient outcomes and overall comfort. Modern medicine is leaning toward closed IV systems that reduce contamination risk.

6. Best Practices for IV Insertion and Care
After you decide which vein you will use, employ proper IV insertion technique, site stabilization, and monitoring.
First, clean the site with alcohol, letting it dry before insertion. Always make sure you can see or feel the vein. Hold the surrounding skin taut as you insert the needle. Keep the bevel up so that the sharpest part enters first.5
Implement infection control practices. Always wash your hands and don clean gloves before coming in contact with the patient and equipment.
Following a catheter replacement schedule prevents contamination from spreading. Check the IV line regularly for signs of infection. Doctors recommend changing adult peripheral IV catheters roughly every 72-96 hours. Replace central lines less often to prevent complications.
Our store is a reliable source for IVs, needles, and related infusion equipment. Explore the variety of Vitality Medical IV supplies and catheters to find the right product for your needs.
Conclusion
Appropriate catheter selection is important, as it ensures safe infusion therapy. The proper gauge size maintains patient comfort and efficient IV access.
Understanding color codes, gauge sizes, flow rates, catheter design, and IV care procedures supports better clinical outcomes. Effective infusion treatment is dependent upon the type of supplies you decide to use.
Vitality Medical is a trusted source for IV catheters and infusion supplies for both professional and home care environments.
Footnotes
1 "Denex International (2023, December 13)." A Comprehensive Guide: IV Cannula Sizes,Colors, Flow Rates and Usage.
2 "Registered Nurse RN." IV Gauges and Colors Chart and Mnemonic.
3 "Modern Physics." Poiseuille’s law.
4 "This vs. That." PTFE vs. Polyurethane.
5 "Nurselabs (2024, August 9)." 50+ Tips & Techniques on IV Insertion.


Login and Registration Form